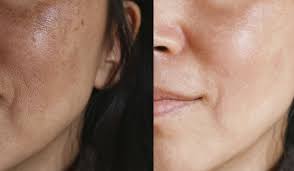
**How Chemical Peels Can Make Your Skin Perfect**
Chemical exfoliation has become an essential step in modern skin care, with acids like AHA and BHA replacing harsh manual exfoliants. But what exactly are these peels? And how do they affect your skin? Let’s break it down.
### What are chemical peels?
Chemical peels are acids that dissolve dead skin cells, excess sebum, and dirt that can lead to breakouts and a dull complexion. Unlike physical exfoliants, these acids require no scrubbing, providing a gentler, more even exfoliation. They help keep the surface of your skin smoother and healthier.
### How do chemical peels work?
When these acids are applied to the skin, they penetrate deeper and dissolve the “glue” that holds dead skin cells together. This process reveals fresher, younger-looking skin. Fruit acids like glycolic and lactic acid work on the outer layer of the skin to promote a radiant complexion by removing dead skin cells and reducing fine lines. BHAs like salicylic acid can penetrate deeper into pores to remove dirt, oil, and bacteria that cause blemishes and acne.
While the idea of using acids may sound intimidating, these formulas are safe and effective when used correctly.
### Types of Chemical Peels
There are different types of acids used in chemical peels, each suited to different skin needs:
– **Glycolic Acid:** Suitable for normal to oily skin. It helps exfoliate and clear clogged pores, making them appear smaller.
– **Malic Acid:** A lesser-known AHA that can revitalize dull skin for a more radiant complexion.
– **Lactic Acid:** A gentle acid that’s ideal for dry or sensitive skin, moisturizing while removing flakes.
– **Salicylic Acid:** A type of salicylic acid that targets deep layers of the skin, opening pores and preventing breakouts.
To avoid irritation, test any new product before using it completely, and consult a dermatologist if in doubt.
### How to Use a Chemical Peel
– **Cleansers:** Typically contain lower concentrations of acids and are suitable for daily use.
– **Toners:** Have higher acid content, so start with 2-3 times per week and adjust usage based on skin reaction.
– **Serums:** Use according to product instructions as concentrations can vary greatly.
– **Masks:** Use 2-3 times per week to avoid irritation.
Overuse of chemical peels can cause dryness or sensitivity, so moderation is key.
### Can I Use a Mask After a Chemical Peel?
If you decide to use a mask after a chemical peel, make sure it does not contain any added acids or irritating ingredients. Allow your skin to regenerate for about 20 minutes before applying a hydrating mask or cream.
### Can I Use a Chemical Peel Around My Eyes?
The skin around my eyes is sensitive, so it’s best to avoid strong acids. Gentle products like low-concentration glycolic acid or hydrating ingredients like hyaluronic acid are safer choices for this area.
### How quickly can you see results?
Results vary, but many users notice smoother, more radiant skin within a week. Over time, continued use can reduce blemishes, fine lines, and dullness. However, results depend on skin type and concerns.
—
**Understanding Oily Skin**
The most important thing about treating oily skin is balance. While it may seem easy to deal with, excess oil can lead to clogged pores, breakouts, and enlarged pores. However, there is an upside to oily skin—it ages more slowly than dry skin.
### What causes oily skin?
Oily skin occurs when the sebaceous glands produce too much sebum. Triggers include genetics, hormones, stress, and diet. This can lead to shiny skin, enlarged pores, and frequent breakouts, especially in the T-zone (forehead, nose, and chin).
### How to Deal with Oily Skin
Even if you can’t stop sebum production completely, you can keep it in check with the right skincare routine:
– **Cleansing:** Use a gentle cleanser with salicylic or glycolic acid to control sebum production and prevent clogged pores.
– **Toning:** Avoid astringents with alcohol, which can dry out the skin and stimulate sebum production. Instead, use a calming agent like witch hazel.
– **Moisturizing:** Even oily skin needs moisture. Look for an oil-free, lightweight moisturizer.
– **Exfoliating:** Exfoliate once a week to prevent clogged pores.
### Dealing with Rashes on Oily Skin
Blemishes are often caused by a mix of excess oil, dirt, and bacteria that clog your pores. Using products with salicylic acid can help clear these blockages. However, be mindful of the strength of the product to avoid drying it out.
### Preventing Sebum Deposits During the Day
Oily skin produces sebum throughout the day. To combat this, use a matte foundation, apply makeup sparingly, and bring oil-blotting papers to soak up excess shine.
### Makeup Tips for Oily Skin
When choosing makeup for oily skin, opt for oil-free, water-based formulas and set with a light powder. Avoid heavy foundations, which can clog pores. Rather than slather foundation all over your face, target blemishes.
### Moisturizers for Oily Skin
Never skip moisturizing. Oily skin still needs moisture, so opt for an oil-free gel moisturizer that won’t disrupt your skin’s oil balance.
### Can I Use Facial Oils for Oily Skin?
Yes, certain oils can benefit oily skin by restoring balance and strengthening the skin barrier. Look for oils like tea tree oil (for blemishes) or rose oil (for moisturizing). Avoid comedogenic oils like coconut oil, which can clog pores.
—
By understanding the science behind chemical peels and following a proper skin care routine, you can manage oily skin and achieve a clearer, more balanced complexion. Follow your daily routine, use the right products, and remember that results take time.
DQH Knowledge drop: In your 20s, your skin cell turnover decreases. (Cell turnover is a key component in keeping your skin youthful.) You know what else slows down? Your collagen production. Starting in your 20s, collagen decreases by about 1 percent per year. Should you want to prevent fine lines and wrinkles, start by eliminating behaviors that contribute to premature aging. “If it’s bad for you, it’s bad for your skin,” says dermatologist Michel Somenek.
“Cigarette smoking reduces blood flow to the skin and causes premature wrinkling and a dull skin texture. Making the repeated pursed motion to inhale can also cause smoker’s lines. Alcohol and recreational drugs are toxins for the skin that damage its cellular structure and DNA,” Somenek tells us. “The faster you eliminate vices while you are young, the better chance your skin and body have to recuperate.” Also, adopting an anti-aging routine in your 20s is key. After all, the best offense is a good defense. We spoke to Somenek and experts Joshua Ross and Audrey Kunin to find out more.
Keep reading for the best anti-aging products for your 20s, according to skincare professionals.
Sunscreen
“We all know that the sun is the number one cause of skin aging and starting the prevention in your 20s is very important,” Ross says. “The majority of your sun damage won’t start to appear until you’re in your 30s, so don’t wait until you see it surface or you’ll be behind the curve. Stay ahead of it with a good-quality zinc-based sunscreen worn daily.”
Farmacy Green Defense Daily Mineral Sunscreen
An invisible sunscreen with SPF 30, plus botanical extracts meant to protect skin with tons of antioxidants. Bonus: It’s clean and fine to use under makeup.
Bareminerals Complexion Rescue™ Tinted Moisturizer Broad Spectrum SPF 30
Although we recommend you use your SPF and moisturizer separately, we also understand moments when you don’t have time or energy for that extra step. For those times, this bareMinerals moisturizer is a great thing to have on hand.
Vitamin C Serum
“A great introduction to anti-aging is to start with a vitamin C serum in your morning skincare routine,” Ross says. “It’s a powerful antioxidant that will neutralize free radicals and brighten the skin.” He adds that it’s a great way to counteract the effects of the sun’s harmful rays, which, as previously mentioned, are among the biggest causes of premature aging.
Drunk Elephant C-Firma™ Vitamin C Day Serum
The Drunk Elephant C-Firma is a lightweight serum that promises to give skin a glow by combining the brightening powers of vitamin C with ferulic acid, l-ascorbic acid, and vitamin E. The included sodium hyaluronate is meant to replace hydration loss, so you shouldn’t have to deal with any irritation.
Sunday Riley C.E.O. Rapid Flash Brightening Serum
This potent serum is jam-packed with vitamin C (15 percent, to be exact), which means it’s a potential superstar at both brightening skin and dousing it in antioxidants.
Peptides
Using peptides on your skin has many benefits, says Somenek. “The skin barrier is what defends the body against pollution, UV rays, bacteria, and toxins. It can be damaged by several everyday factors. Using topical peptides aids in building a stronger barrier,” he says. “Peptides comprise elastic fibers, which are a type of protein. These fibers help to make skin appear taut and firm. Peptides can also help repair damaged skin, relieve inflammation, and even out skin tone. Some peptides can kill acne-causing bacteria that is common in 20-somethings.”
Kunin agrees, saying, “Peptides are an excellent entry point for supporting collagen.” She recommends looking for face and eye treatments that contain these collagen-boosting powerhouses.
Charlotte Tilbury Magic Eye Rescue Cream
This Charlotte Tilbury super-emollient eye cream has a base of coconut oil and shea butter (read: it’s incredibly hydrating). Botanicals plus peptides are meant to help reduce dark circles and boost collagen, respectively.
This creamy moisturizer serves up potent collagen-boosting peptides and pycnogenol, and antioxidant-rich vitamin C. “Instead of sitting on top of the skin, peptides penetrate the outer layer so they go deep. The ‘signals’ they send tell the cells to produce elastin and collagen, which are needed for youthful-looking skin,” explains Somenek.
At-Home Peel Pads
Remember that skin cell turnover fiasco we talked about earlier? One way to help support it is by exfoliating. “Exfoliation is important to help keep skin fresh and luminous,” Kunin says. She recommends using at-home peel pads as an easy and effective way to exfoliate.
“The goal in your 20s is to fight the slowing pace of cell turnover. It is wise to use products that gently exfoliate, yet still remove oil and other impurities. Products that have Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHA) or Beta Hydroxy Acids (BHA) are a good choice.”
According to Somenek, you should only exfoliate two to three times a week. “People of all ages are guilty of over-exfoliating and that can be too much of a good thing,” he says.
Dermadoctor Kakadu C Intensive Vitamin C Peel Pad
A few swipes of this Derma Doctor powerful peel pad promise to leave your skin glowing and smooth, thanks to the seven (yes, seven) types of chemical exfoliants, including AHA and BHA. It also contains vitamin C via Kakadu plum extract for added brightening and antioxidant protection.
KEY INGREDIENTS Kakadu plum extract is sourced from the Kakadu plum, a fruit grown in northern Australia. It contains vitamin C, which restores the skin’s natural barrier, increases collagen production, and soothes irritation.
Dr. Dennis Gross Skincare Alpha Beta® Universal Daily Peel Pads
These are the gold standard of peel pads, with a cult following and over 900 five-star reviews on Sephora. They’re easy to use and contain a blend of anti-aging exfoliating acids.
Emollient Night Cream
“In your 20s, you need to start upping the hydration in your skincare routine. You may have been cautious of over-moisturizing because of acne in your teens, but as you enter your 20s, your skin transitions and becomes drier,” Ross says. “I recommend an emollient night cream added into your evening skincare regimen.”
“Twenty-somethings need to make sure that they are not using creams that will clog their pores and cause excess oil production,” says Somenek. Opt for non-comedogenic products.
Cerave Skin Renewing Night Cream
One great choice is the CeraVe Skin Renewing Night Cream, which is a non-comedogenic night cream that leaves skin soft and glowy. It combines the moisturizing powers of ceramides and hyaluronic acid.
RoC Retinol Correxion Max Hydration Creme
“The best night cream ingredients contain retinol, benzoyl peroxide, and/or salicylic acid or hyaluronic acid. The goal is to moisturize, yet remove excess oil,” says Somenek. This Roc Retinol Correxion cream fits the bill as it contains both hyaluronic acid and retinol so it promises to moisturize while also being non-comedogenic.