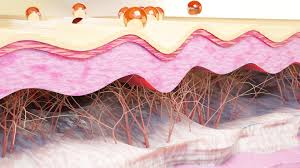
Elastin in Skin
Elastin is a protein that gives skin its snap and elasticity. It allows skin to stretch and then bounce back into place without getting loose or saggy. Elastin is a major component of elastic fibers in the skin. Elastic fibers are like little coils or springs that give skin its stretchiness.
Elastin vs Collagen
The dermis contains mainly collagen and elastin. Collagen provides strength, thickness, firmness and texture. Elastin provides firmness and recoil. Both are vital for healthy, youthful looking skin:
Collagen = structure and shape
Elastin = stretch and elasticity
As we age, collagen and elastin both decline. But elastin cannot be replenished like collagen can. Treatments for sagging skin need to focus on replacing collagen, not elastin.
How Elastin Works in Skin
Elastic fibers are found throughout the dermis, the deeper layer of the skin. The dermis contains collagen fibers which provide structure, and elastic fibers which provide stretch and recoil. These fibers allows the skin to stretch and then snap back into shape. This elasticity keeps skin looking firm, toned and youthful. As we age, elastin levels decline leading to loose, sagging skin.
The best way to keep your skin from sagging is to wear SPF and keep the skin moisturized with antioxidants.
[[M08,M23,M25]]
How elastin works
Elastin Production in Skin
It is produced by fibroblasts in the dermis. It starts off as soluble molecules called tropoelastin which are secreted by fibroblasts. These tropoelastin molecules join together and attach to microfibrils to form elastic fibers.
This process is called elastogenesis. It mainly happens during infancy and childhood when skin elasticity is developing. After puberty, elastin production decreases dramatically. The elastin and elastic fibers made in youth have to last a lifetime.
Where in Skin in Elastin?
Elastic fibers are found throughout the dermis, running parallel and perpendicular to the skin surface. This web-like arrangement of elastic fibers maintains elasticity in all directions.
The papillary dermis near the surface contains fine elastic fibers called oxytalan fibers extending perpendicular to connect to the epidermis. Oxytalan fibers contain the microfibrillar protein fibrillin but no elastin.
The deeper reticular dermis houses thicker elastic fibers composed of both elastin and fibrillin called elaunin fibers running parallel to the surface. This intricate network of oxytalan and elaunin elastic fibers is critical for healthy, youthful skin that does not sag.
Structure of elastin
Structure of Elastin
It has a coiled structure that allows it to stretch and recoil. This unique structure is due to high levels of glycine, valine, alanine and proline in the protein. Water also plays a role, allowing the coiled elastin molecules to extend and contract.
The important role water plays is why moisturizing and hydrating the skin is important to help prevent damage of elastin fibers.
Breakdown and Damage to Elastin Fibers
Elastin has extremely low turnover in adult skin. This means that not very much new elastin can be made in adult skin. So we must protect the elastin we have. The elastic fibers made in youth are pretty much expected to last a lifetime.
Elastin is susceptible to damage and degradation from:
Sun exposure (UV radiation)
Excessive heat
Normal aging
Environmental factors like pollution
Rapid weight gain
Excessive skin stretching
Elastase and other Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) – enzymes that break down elastin
Free radicals
Sun exposure in particular causes dramatic changes and breakdown of elastic fibers. This leads to permanently loose, sagging skin on sun-exposed areas.
How to increase elastin in skin
Increase Elastin in Skin
New elastin synthesis shuts down after puberty. This means that there are no treatments that can increase the elastin in skin.
Lasers don’t work
Radiofrequency does not work
Skin care products do not work.
Your only option to truly tighten skin and remove excess skin is plastic surgery to remove the loose skin.
Skin tightening treatments can shrink and tighten collagen, but no treatments work on elastin although many claim they do.
Why companies claim their products can increase elastin
To understand how companies can make this claim, you need to understand how elastin in skin is measured. The measuring devices we use are imperfect and can show improvement in elasticity or elastin content. But we know from basic science studies that adult skin makes very little elastin so these measurements are incorrect.
How to measure elastin levels
Measuring Elastin Levels and Skin Elasticity
Below I discuss potential limitations of elastin measuring devices and technologies. In addition to the downsides of each technology listed below, there are other issues that could make these techniques inaccurate including:
Sampling error – Single biopsies or ultrasound spots may not represent whole skin.
Inter-rater variability – Results depend on the technician’s skill.
Qualitative, not quantitative – They show arrangement of fibers but not absolute amounts.
Limited depth penetration – Confocal and ultrasound can only image superficial dermis.
So while these methods are useful, there are several variables that can affect accuracy and consistency of results. Quantitative biochemical assays directly measuring elastin content would be more definitive, but it would be better is a biopsy was not required to gather results.
Cutometer
This device measures the elasticity of skin by suctioning the skin and measuring how well it returns to its original position.
Higher elastin levels lead to better elastic recoil. However, it is very technique dependent and can be variable between users. It also only measures a small area of skin.
This elasticity measurement is usually done 3 times and the results averaged. However, each time the skin is stretched, it looses a bit of recoil – so doing this measurement multiple times decreases accuracy. You could do the measurement one time and that would give a more elastic result than if you did it 3 times and averaged it. This makes it easy for researchers to manipulate the results. Even if they are consistent with how they use this device, the results are not extremely accurate.
Elastin stains
Skin biopsies can be taken and stained to look for elastin levels. Buy here is the problem with that: injury can distort the presence of elastin so when you d the rebiopsy you must g to a different area- and that area might not have had the same baseline level of elastin. It is impossible to biopsy the skin twice in the exact same area because the act of biopsying changes the skin’s components. However, these staining methods are the ones most frequently used to look at elastin levels. They give a qualitative result rather than a quantitative one.
Verhoeff’s stain and other specialized stains are used on skin biopsy samples to highlight elastin fibers and determine elastin content. However, biopsies are invasive, examine only a small area, and stains may introduce artifacts.
Laser scanning confocal microscopy
This advanced imaging technique uses antibodies to specifically stain for elastin. It can visualize the 3D arrangement of elastic fibers in the skin. However, it requires biopsies, has limited depth penetration, and results depend heavily on staining technique.
High-frequency ultrasound
Ultrasound at very high frequencies (>20MHz) can detect and measure elastic fibers in skin. However, it is very sensitive to probe pressure and hydration. Resolution may also not be high enough to measure fine fibers accurately.
Reviscometer
This instrument measures skin viscoelasticity using acoustic shear waves. It can demonstrate differences in skin elasticity with age. However, results depend on careful control of multiple parameters.
Dermaflex
This suction device also measures elastic properties of skin. However, it uses a different technique than the Cutometer and is less commonly used for cosmetic research.
Protecting and preserving elastin
Protecting and Preserving Elastin
Since elastin can’t be replenished, skin care should focus on protecting the elastin you already have:
Use broad spectrum sunscreen daily to prevent UV damage
Use gentle cleansers and moisturizers to maintain skin’s barrier
While claims abound, there are currently no skin care ingredients clinically shown to increase elastin. Protecting your existing elastin is key to maintaining youthful, elastic skin over time.
The best way to preserve elastin in skin is to use the best skin care products for your skin type to reduce inflammation, free radicals and MMPs that can cause elastin breakdown. Make sure you are using the best products to preserve your elastin by shopping using your Baumann Skin Type.
Natural Way to Protect Elastin
Protec your skin’s elastin from the inside and outside.
Things you can do to help skin stay firm and keep its recoil abilities:
Eat a healthy, balanced diet with antioxidants to combat free radicals
Avoid smoking which damages skin proteins like elastin
Avoid excessive sun exposure
Wear sun protective clothing
Wear SPF
Keep skin hydrated with moisturizers to keep elastin from being injured when stretched
Moisturize the body with antioxidant oils
Elastin in Diet
Unfortunately, there are no dietary sources of elastin. Elastin is made up of amino acids like glycine, valine, proline and alanine. You can get these amino acids by eating:
Meat, poultry, fish, eggs
Dairy
Nuts and seeds
Legumes
Whole grains
But eating foods rich in these amino acids won’t boost elastin levels. Elastin production is complex and can’t be increased by diet once it shuts down after puberty.
To protect your skin’s elastin eat a diet rich in antioxidants and low in sugar because sugar can cause glycation of elastin, leading to damage. (11)
Elastin in your diet
Elastin Supplements
There are no supplements that will increase skin elastin because your skin cannot make new elastin after puberty.
The only way to improve skin elasticity with supplements is hydrate the skin which makes the remaining elastin in skin more supple and have better recoil. Glucosamine supplements may help by increasing hyaluronic acid in skin. Using a topical moisturizer with humectants is also a good idea.
[[M38]]
Summary
The takeaway is that elastin is a critical protein that gives skin its snap, resilience and elasticity. Unfortunately, we cannot replace elastin once it is lost as we age. That’s why it is so important to protect the elastin you already have! Use broad spectrum sunscreen daily, eat a healthy diet with antioxidants, don’t smoke, and be gentle with your skin. Follow a customized skin care routine matched to your Baumann Skin Type with ingredients like humectants, antioxidants, anti-inflammatories and retinoids. Your skin care regimen is your best defense against elastin breakdown. Guard your elastin levels and you’ll be rewarded with healthy, youthful, elastic skin for years to come.


